Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ)
HCQ in pediatric ILD
Interstitial lung diseases in children (chILD) are a group of more than 200 entities, all of which are rare or ultra-rare.
No successfully proven pharmacological treatments are available up-to-date. All current pharmacological treatment regimens dependent mainly on trial and error and anecdotal reports. Besides systemic steroids in particular hydroxychloroquine is most frequently tried for treatment.
Due to the rareness of the diseases only international studies can collect sufficient numbers of patients.
 The HCQ-study
The HCQ-study
The chILD-EU project will implement a study that allows the determination of the efficacy of hydroxychloroquine in this population of children. This study will consist of two blocks, one which observes the beginning (START) and one that observes the end of treatment (STOP):
START randomized controlled in parallel-group, then switch placebo to active drug,
STOP randomized controlled in parallel-group
This international study will address all important aspects of hydroxychloroquine treatment in child and will help to create new knowledge for everyday care in this broad group of pediatric interstitial lung diseases.
 Study aims
Study aims
- Evaluate the efficacy of hydroxychloroquine against placebo in chILD
- Evaluate the safety of mid-term use of hydroxychloroquine
- Be able to make a decision on the risk and benefit of the use of hydroxychloroquine
- Help standardizing the pharmacological treatment of chILD
Who can take part in the study?
1) Stable baseline during “run in” / no changes in other medications
2) Patients diagnosed with chILD (= diffuse parenchymal lung disease (DPLD)), defined as:
a) chILD genetically diagnosed (all ages including adults or previously preterm babies)
disease causing mutations in SFTPC, SFTPB, ABCA3, TTF1 (Nkx2-1)
further extremely rare entities with specific mutations, for example in TBX4, NPC2, NPC1, NPB, COPA, LRBA and other genes
b) chILD histologically diagnosed (adults < 30 years)
Chronic pneumonitis of infancy (CPI)
Desquamative interstitial pneumonitis (DIP)
Lipoid pneumonitis
Cholesterol pneumonia
Nonspecific interstitial pneumonitis (NSIP)
PAP after the exclusion of mutations in GMCSF-Ra/b and GMCSF autoantibodies
Usual interstitial pneumonitis (UIP)
Follicular bronchitis/bronchiolitis/Lymphocytic interstitial pneumonia (LIP) unless associated with immunodeficiency
Storage disease with primary pulmonary involvement (e.g. Niemann Pick)
Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome
Idiopathic pulmonary haemorrhage (haemosiderosis)*
Other histology diagnosing chILD, in particular combination of the above pattern, but not exclusively
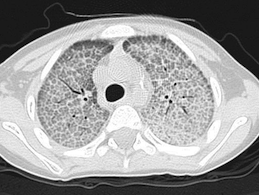
*may be diagnosed in the absence of a lung biopsy by characteristic lung lavage cytology (PAS stain, Fe stain), CT pattern or autoantibodies (gliadin, endomysium; cANCA) and clinical course.
If you are interested in taking part in the study or if you have any questions please contact for further information.

